The Link Between Acute Scaphoid Fractures and Sports Injuries
What is an Acute Scaphoid Fracture?
An acute scaphoid fracture refers to a break in the scaphoid bone, one of the small bones in the wrist.
The scaphoid bone is situated on the thumb side of the wrist and is a critical component of the carpal bones. It helps maintain the normal, pain-free motion of the wrist, which is required in many athletic activities.
Fractures of the scaphoid are common injuries, often the result of a fall onto an outstretched hand.
What are the Types of Acute Scaphoid Fractures?
Acute scaphoid fractures can be classified into two main types based on the displacement of the fracture fragments:
- Acute nondisplaced scaphoid waist fractures: In a nondisplaced scaphoid fracture, the bone fragments remain in their normal anatomical alignment, with no significant separation.
- Acute displaced scaphoid waist fractures: Displaced scaphoid fractures involve separation or misalignment of the fracture fragments. They are often associated with a higher risk of complications.
What is the Link Between Acute Scaphoid Fractures and Sports Injuries?
The link between acute scaphoid fractures and sports injuries is notable due to the unique vulnerability of the scaphoid bone in the wrist during certain athletic activities, such as:
- Contact or jumping sports, such as football, soccer, basketball, boxing, and wrestling, can elevate the risk of scaphoid injuries.
- Sports in which falling onto an outstretched hand is common, like snowboarding, skiing, and rollerblading, can impact the wrist, resulting in scaphoid fractures.
- Athletes engaged in repetitive wrist movements, including gymnasts or weightlifters, may experience cumulative stress on the scaphoid, making it susceptible to fractures over time.
What are the Symptoms of Acute Scaphoid Fracture?
The symptoms of an acute scaphoid fracture can vary, but common signs include
- Persistent, dull ache in the radial part of the wrist.
- Aggravated pain by pinching and gripping.
- Localised wrist swelling with fullness in the anatomical snuffbox.
- Localised bruising.
- Tenderness on palpation of the radial side of the wrist.
It’s important to note that the symptoms of a scaphoid fracture can sometimes be subtle, and individuals may attribute the pain to a sprain or another minor injury. Since scaphoid fractures can lead to complications, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
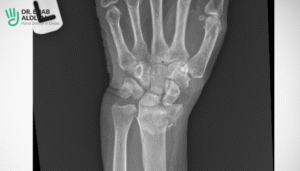
How is Acute Scaphoid Fracture Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of an acute scaphoid fracture typically involves:
- Standard X-rays are often the first-line imaging modality. However, occasionally acute scaphoid fractures X-ray may be deceiving, especially if the fracture is small.
- Advanced imaging studies like MRI or CT scans.
Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial in the case of scaphoid fractures to initiate appropriate treatment and minimise the risk of complications. If there is a suspicion of a scaphoid fracture, individuals should seek medical attention for a thorough evaluation.
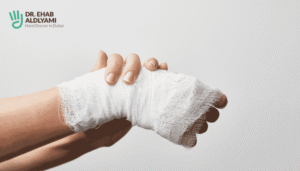
How to Treat Acute Scaphoid Fracture?
The treatment of an acute scaphoid fracture depends upon several factors, including the fracture type, location, and whether or not the fracture fragments are displaced.
Here are general approaches to the treatment of acute scaphoid fractures:
Non-surgical Treatment: Immobilisation
Treatment may involve a splint or cast for a mild scaphoid fracture that is nondisplaced and hasn’t significantly shifted.
Splinting is typically recommended for three to five weeks, while a cast may be required for a longer period, usually six to eight weeks. In both cases, you’ll likely need follow-up X-rays to ensure your bone is healing correctly.
Surgical Treatment: Internal Fixation
In cases where the fracture is significantly displaced or has poor alignment that cannot be adequately maintained with casting, surgery may be recommended.
During the surgical procedure, the surgeon will realign the fractured scaphoid to its proper position, securing it for healing. This often includes internal fixation, where metal pieces are inserted into the bone to keep it stable as it heals and fuses back together.
Rehabilitation Post Treatment
a) Physiotherapy: After immobilisation, whether post-surgery or conservative treatment, the hand and wrist may experience stiffness and reduced muscle strength. Physiotherapy aims to achieve:
- Restore active range of movement
- Reduce swelling
- Increase grip and wrist strength
- Facilitate return to functional goals and tasks
b) ROM Exercises: In the early stages of post-immobilisation, emphasise active-assisted range of motion (ROM) exercises to address stiffness in the hand and wrist. These exercises focus on wrist and thumb movements and address potential stiffness in fingers, elbows, and shoulders.
c) Strengthening Exercises: After achieving full or functional active range of motion, engaging in wrist and hand strengthening exercises is crucial. This step is vital in rehabilitation as neglecting hand strengthening may lead to lasting functional deficits and increase the risk of further injury.
Contact Dr Ehab Bassim Aldlyami for Scaphoid Fractures Treatment in Dubai
When it comes to scaphoid fracture treatment, Dr Ehab Bassim Aldlyami stands out as a trusted specialist in Dubai. With a focus on personalised care, Dr Ehab combines his extensive experience with the latest advancements to offer tailored treatment options for wrist and hand injuries.